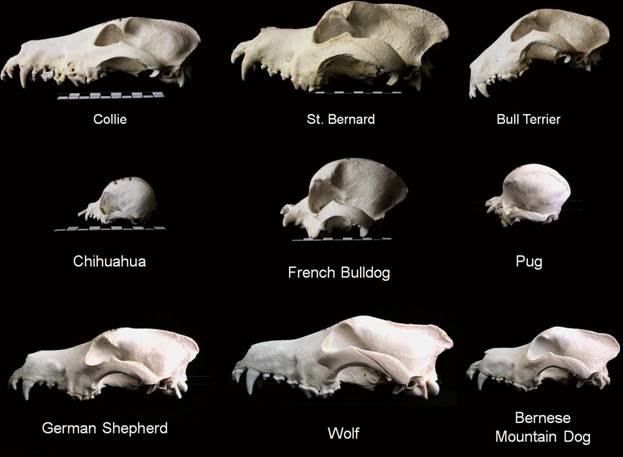
When did wolves become dogs?
What evolutionary and developmental processes are involved in creating physical variation?
Is selection responsible for moulding the diversity of life?
Or does developmental bias via drive and constraint determine how animal shapes change?
Abby Drake is interested in the processes that produce macroevolution and dictate which physical appearances, evolve and which do not.
She is especially interested in learning how species evolve: What mechanisms produce enough physical or behavioural change to ensure reproductive isolation on the population level?
To this end, she studies developmental processes that lead to large modifications of morphology, using variation in vertebrate skulls to answer these questions.
Abby uses three-dimensional scan data to capture each specimen’s 3D geometry.
This type of data allows her team to look at the shape of the skull holistically using a sophisticated shape analysis called geometric morphometrics.
While she also works on cetaceans, owls and primates, this episode focuses on her extensive work examining canids: when did wolves become dogs, how have we shaped them, and where might they go in the future?
Podcast
Images
Video
Publications

Drake, A. G., Coquerelle, M., & Colombeau, G. (2015). 3D morphometric analysis of fossil canid skulls contradicts the suggested domestication of dogs during the late Paleolithic. Scientific reports, 5.
Drake, A. G. (2011). Dispelling dog dogma: an investigation of heterochrony in dogs using 3D geometric morphometric analysis of skull shape [PDF]. Evolution & Development, 13(2), 204-213. **If you download and open this pdf with Adobe Reader 9 or higher you can rotate and magnify the skulls in the figures.
Drake, A. G., & Klingenberg, C. P. (2010). Large‐scale diversification of skull shape in domestic dogs: disparity and modularity. The American Naturalist, 175(3), 289-301.
Drake, A. G., & Klingenberg, C. P. (2008). The pace of morphological change: historical transformation of skull shape in St Bernard dogs. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 275(1630), 71-76. http://www.skidmore.edu/biology/faculty/ProcRSoc2008.pdf
Links
Abby Drake: ResearchGate Profile
Abby Drake on Twitter: @AbbyGraceDrake
Daily Mail (UK): 30,000 year-old fossil of the oldest dog turns out to be a wolf
CBS News: When did dogs become man’s best friend?
Biologist Drake helps answer key question in canine history: Skidmore College News